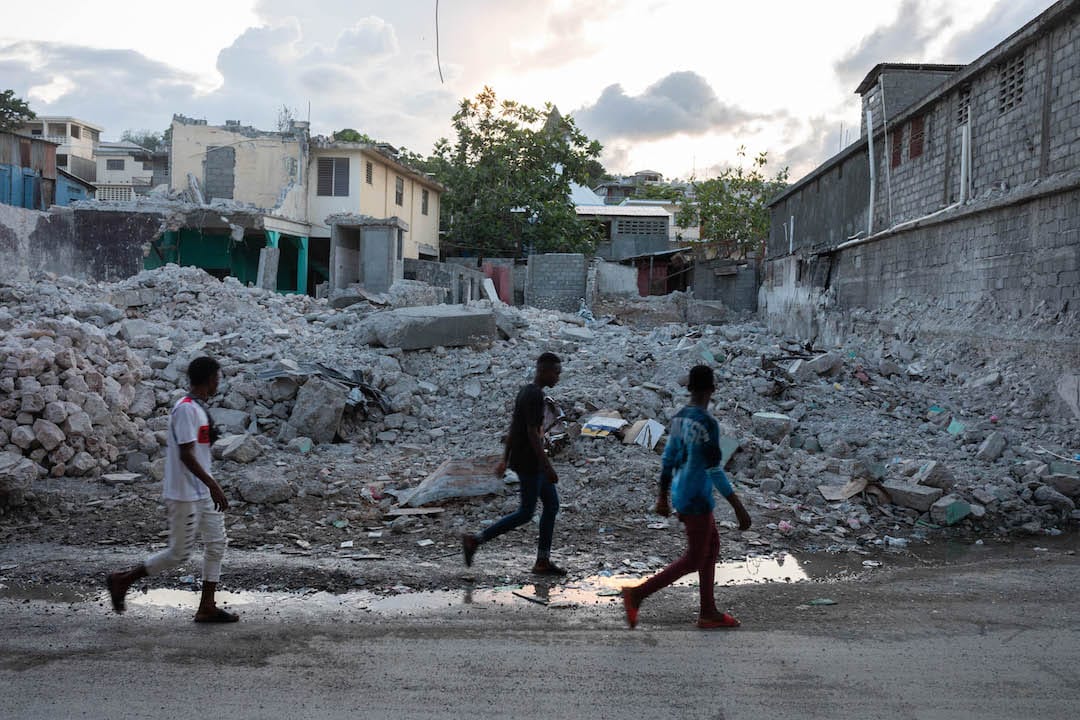Doctors Without Borders, or Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF), has been a critical presence in Haiti for decades, providing medical assistance in one of the world’s most under-resourced and disaster-prone countries. However, the organization recently announced its decision to scale down and leave the country. This decision has raised several questions, particularly regarding the challenges that prompted this move and what it means for Haiti’s healthcare system, as well as for the broader humanitarian context. This article will explore the reasons behind MSF’s departure from Haiti, the impact on the country, and the future of healthcare in the region.
A Long History of Support in Haiti
MSF has a longstanding presence in Haiti, dating back to the early 1990s when the country was facing multiple health crises, including cholera outbreaks, the aftermath of the 2010 earthquake, and various infectious diseases. The organization’s mission has been to provide medical care in conflict zones, during epidemics, and in underserved regions, and it has gained recognition for delivering services in some of the most challenging environments.
In Haiti, MSF has operated hospitals, clinics, and mobile health units, providing emergency medical care, maternal and child health services, surgical interventions, and treatment for conditions like tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS. Its doctors and staff have worked tirelessly in both the capital, Port-au-Prince, and rural areas, where healthcare is scarce. However, the decision to scale down operations and withdraw from some parts of Haiti is a reflection of the increasingly difficult conditions in the country, which have made it harder for MSF to carry out its mission effectively.
Challenges Faced by MSF in Haiti
The decision to leave Haiti has been driven by a confluence of political, security, and logistical challenges, which have significantly impacted MSF’s ability to operate. While the organization has made it clear that it will continue to support certain medical programs in Haiti, the broader withdrawal is indicative of the worsening situation in the country.
1. Escalating Violence and Insecurity
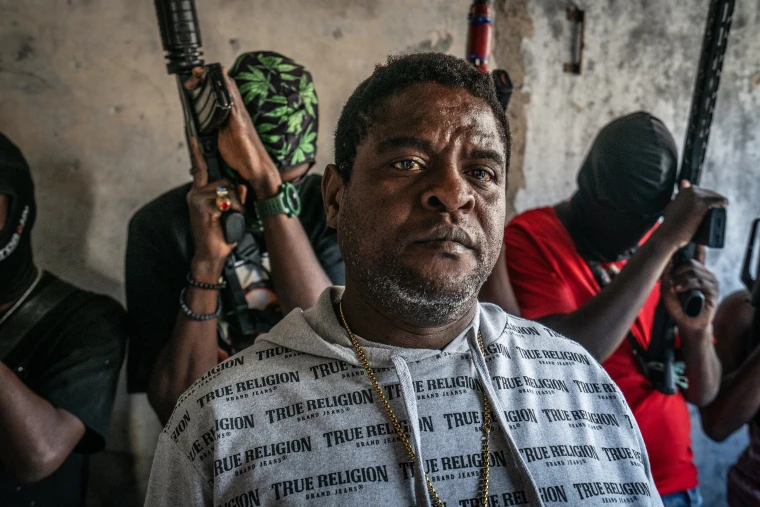
Over the past few years, Haiti has seen an alarming rise in gang violence and political instability. Gangs have taken control of large swathes of the capital and other parts of the country, making it difficult for healthcare workers to safely operate. In particular, hospitals and clinics have been targeted by armed groups, while healthcare workers face the constant threat of violence. MSF has reported several incidents where their staff and facilities were directly impacted by this violence, making it increasingly difficult to deliver care.
The rising levels of violence have created a sense of insecurity that affects all aspects of life in Haiti, and the safety of aid workers has become a major concern. MSF’s primary goal has always been to provide medical care in areas where it is most needed, but the deteriorating security situation has hampered their ability to do so effectively.
2. Political Instability and Weak Governance
Haiti has faced years of political unrest, with a lack of stable governance exacerbating the country’s systemic issues. The assassination of President Jovenel Moïse in 2021 further plunged the country into chaos, sparking protests, violent uprisings, and a breakdown of law and order. Political instability has led to a lack of coordinated response to the country’s pressing needs, particularly in healthcare.
With weak government institutions and no clear path forward for political reconciliation, it has been difficult for organizations like MSF to collaborate effectively with the Haitian government or local authorities. The lack of a stable governance structure has complicated the provision of essential services, including healthcare. MSF has been forced to rely heavily on its own networks and resources, but this is no longer sustainable as the country faces increasing challenges.
3. Economic Collapse and Resource Shortages
Haiti’s economic collapse has also played a significant role in MSF’s decision to scale down its operations. The country is one of the poorest in the Western Hemisphere, with widespread poverty affecting access to food, clean water, and healthcare. Inflation, the devaluation of the local currency, and a lack of basic resources have made it even harder to sustain essential healthcare services.
MSF has long faced challenges in providing healthcare in Haiti, but the recent economic crisis has intensified these difficulties. Resources, including medical supplies and staff, have become more scarce, and MSF has struggled to meet the increasing demand for services. The organization’s ability to operate in the country has been further constrained by a lack of infrastructure and support from local institutions, which are themselves severely underfunded and overstretched.
4. Epidemics and Healthcare Strain
Haiti has been the site of multiple health emergencies, including the cholera outbreak that began in 2010 after the devastating earthquake. While the situation has improved, Haiti remains vulnerable to infectious disease outbreaks, and the healthcare system remains weak and underdeveloped. MSF’s response to such outbreaks has been vital, but the challenges of managing such crises have become more complex due to the other factors at play.
The COVID-19 pandemic also placed an additional strain on Haiti’s already fragile healthcare system, further stretching resources and complicating the delivery of medical services. MSF’s withdrawal is partly a recognition that despite its best efforts, it is no longer possible to operate at the same level in a country where the overall healthcare infrastructure is failing.
Impact of MSF’s Departure on Haiti
The departure of MSF from Haiti is a major blow to the country, as the organization has been a lifeline for many of the most vulnerable people in the country. Its medical teams have provided emergency care, run mobile clinics in remote areas, and delivered vaccines and treatments during outbreaks. With MSF’s decision to scale down, it leaves a significant gap in healthcare services that will be hard to fill.
Local hospitals and clinics, many of which are underfunded and understaffed, will be left to manage the growing demand for healthcare with fewer resources. The absence of MSF’s expertise and support will make it even more difficult for these institutions to cope with the ongoing health crises, including violence-related injuries, chronic diseases, and infectious outbreaks.
What Does the Future Hold for Haiti’s Healthcare System?
The challenges faced by MSF are a reflection of broader issues within Haiti’s healthcare system. While the country’s healthcare professionals and organizations continue to work tirelessly, they are operating in a context of political and economic instability that undermines their effectiveness. As MSF pulls back, it will be crucial for the Haitian government, international aid organizations, and local civil society to step up and fill the void left by the organization’s departure.
However, the road ahead is uncertain. Political stability, improved security, and greater investment in healthcare infrastructure are essential for building a sustainable healthcare system in Haiti. Until these systemic issues are addressed, it is unlikely that the country will see significant improvements in health outcomes, and the gap left by MSF’s withdrawal may continue to widen.
Conclusion
The decision of Doctors Without Borders to leave Haiti is a poignant reminder of the challenges faced by humanitarian organizations in countries marred by violence, political instability, and economic collapse. MSF has been a vital provider of medical care for millions of people in Haiti, and its departure underscores the growing difficulty of delivering aid in such a complex environment. While the situation is dire, it also presents an opportunity for the international community to re-examine its approach to Haiti and provide more sustainable support for its healthcare system. The people of Haiti continue to need assistance, and the world must find ways to help them navigate these unprecedented challenges.